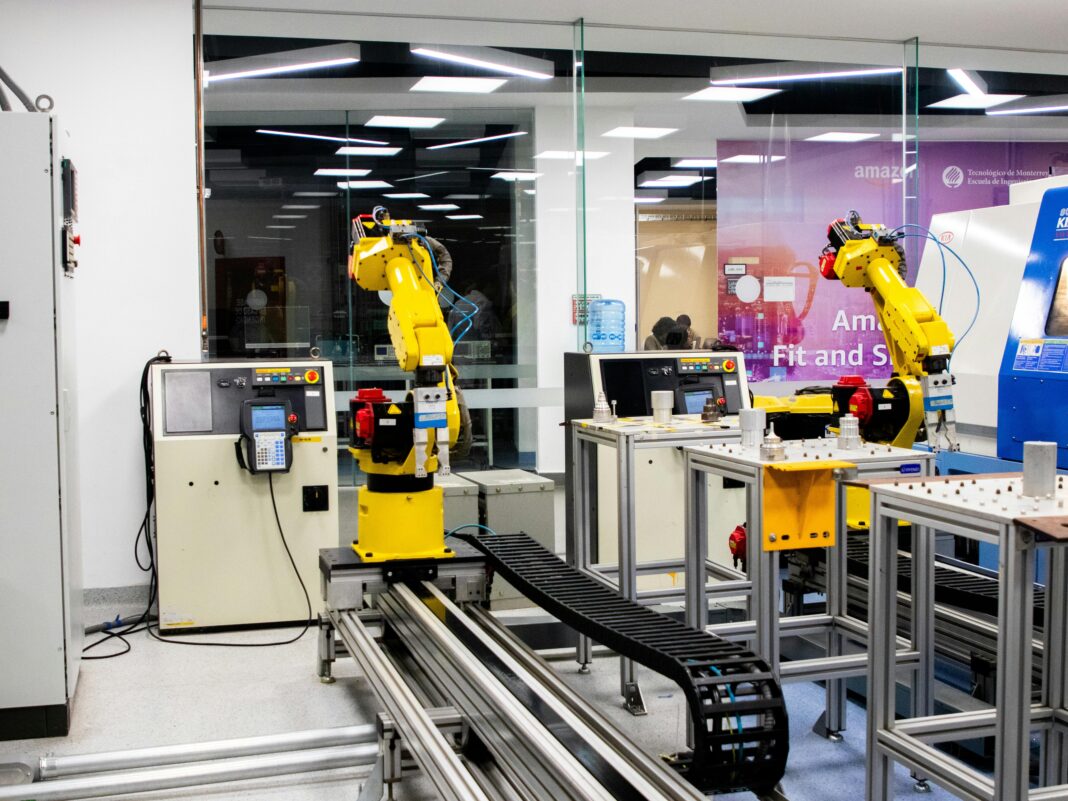
Regarding modern manufacturing and industrial processes, industrial robots are one key player in transforming efficiency and precision. These mechanical marvels have revolutionised industries worldwide, from fully automated assembly lines to intricate pharmaceutical packaging. But what are the types of industrial robots and how exactly do they work, and what makes them so essential?
This guide dives deep into the fascinating world of industrial robots, exploring their various types, applications, and the future trends shaping their evolution. Whether you’re a manufacturer looking to streamline operations, an industrial engineer striving for innovation, or a tech enthusiast curious about robotics, this is your go-to guide.
What Are Industrial Robots?
A Brief History
Industrial robots are automated, programmable machines capable of performing complex tasks with high precision. Their roots trace back to the 1950s, when George Devol invented the “Unimate,” the first industrial robot, which revolutionized the automotive industry. Since then, robotics technology has advanced rapidly, incorporating sophisticated sensors, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
Importance in Modern Manufacturing
Industrial robots are integral to industries that prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and repeatability. They excel in automating repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and increasing production output. From welding and material handling to packaging and quality control, these robots are redefining what’s possible across various sectors.
Types of Industrial Robots
Understanding the types of industrial robots and their unique capabilities can help businesses choose the right robotic solution. Here’s an overview of the most common types:
1. Articulated Robots
Articulated robots are perhaps the most recognizable type, with multiple rotary joints (ranging from two to ten or more). These joints mimic the human arm’s range of motion, making them incredibly versatile.
- Capabilities: Ideal for tasks like welding, assembly, and material handling.
- Limitations: Larger footprint and higher costs compared to other types.
2. SCARA Robots (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm)
SCARA robots specialize in lateral movements, offering speed and precision for assembly tasks.
- Capabilities: Highly efficient for pick-and-place operations, precision drilling, and industrial assembly.
- Limitations: Restricted flexibility, primarily functioning on a single plane.
3. Cartesian Robots
Also known as gantry robots, Cartesian robots operate on three linear axes (X, Y, Z). Their simple design makes them cost-effective and easy to program.
- Capabilities: Commonly used in 3D printing, CNC machines, and packaging.
- Limitations: Limited reach compared to articulated robots.
4. Delta Robots
Delta robots feature a spider-like design and are famous for their lightning-fast speeds and precision.
- Capabilities: Excellent for tasks requiring speed, like food packaging and small electronic assembly.
- Limitations: Best suited for lightweight operations.
5. Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots are designed to work alongside humans without requiring additional safety barriers. They are user-friendly and adaptable to various environments.
- Capabilities: Ideal for SMEs (small and medium-sized enterprises) looking for flexible automation.
- Limitations: Lower payload capacity and speed compared to traditional industrial robots.
These types ensure there’s a perfect robotic solution tailored for every industry need.
Unique Applications of Industrial Robots
Industrial robots have carved out niches in industries far beyond traditional manufacturing. Here are some standout applications:
1. Automotive Assembly Lines
The automotive sector was one of the first to adopt industrial robots, and they remain indispensable for large-scale production. Robots excel at welding, painting, and assembling vehicle components with precision, ensuring quicker assembly times and consistent quality.
2. Pharmaceutical Packaging
Pharmaceutical production requires sterile, precise, and efficient processes. Robots ensure accurate dispensing of medications, error-free labeling, and secure packaging, reducing contamination risks.
3. Food Processing and Agriculture
Delta robots enhance efficiency in food packaging by performing sorting, slicing, and even decorating with incredible speed and accuracy. Meanwhile, cobots are being introduced into agriculture for activities like planting, sorting produce, and even monitoring crop health.
4. Warehousing and Logistics
Robots are playing a critical role in warehousing, improving inventory management, order picking, and material handling. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are frequently employed in large warehouses to optimize supply chain operations.
Advantages and Challenges of Implementing Industrial Robots
Advantages
- Boosted Productivity: Robots operate tirelessly, increasing output and reducing production times.
- Enhanced Safety: They handle hazardous tasks, keeping employees safe from dangerous environments.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation minimizes waste and cuts long-term labor costs.
- Improved Precision: Robots execute tasks with incredible accuracy, ensuring consistent product quality.
Challenges
Despite these benefits, there are challenges to consider:
- High Initial Costs: Purchasing, installing, and programming industrial robots require significant investment.
- Skill Gap: Employees often require training to operate and maintain these systems.
- Integration Complexity: Aligning robotic systems with existing workflows can be technically demanding.
However, advancements in robotics are steadily reducing these barriers, making them more accessible than ever.
Future Trends in Industrial Robotics
The future of industrial robots is brimming with possibilities. Here’s a glimpse into what lies ahead:
1. Integration with AI and IoT
Next-generation robots will leverage AI and IoT to make real-time decisions, adapt to new tasks, and optimize workflows autonomously.
2. Expansion into New Industries
Sectors like healthcare, construction, and retail are starting to incorporate robots for innovative applications like robot-assisted surgeries and automated retail stocking.
3. Impact on the Job Market
While robots may replace certain repetitive jobs, they’re also expected to create new opportunities by driving demand for skilled workers in programming, maintenance, and system integration.
Take the Next Step into the Robotic Revolution
Industrial robots are more than machines; they’re enablers of innovation, efficiency, and growth. By understanding the various types, applications, and future trends of industrial robotics, businesses can stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
If you’re ready to integrate these cutting-edge technologies into your operations, consult with industry experts or reach out to trusted suppliers for tailored solutions. The future of robotics is here—embrace it!

