Wildlife conservation techniques are about protecting animal species and their natural habitats. Furthermore, this means making sure that the ecosystems they live in are preserved, allowing animals to thrive rather than vanish from our planet.
Why does this matter? Simply put, everything in nature is connected. Consequently, when we lose a species, the whole system feels the impact, and so do we. For example, think of bees. They pollinate many of the crops we eat, and without them, our food supply could be in serious trouble. Therefore, wildlife conservation techniques are crucial to keeping these systems balanced.
Definition of Wildlife Conservation
In simple terms, wildlife conservation techniques means efforts to protect animals and plants, particularly those that are endangered. This includes creating protected areas, like national parks, and laws that prevent over-hunting and habitat destruction. It’s about giving the planet a fighting chance.

Beyond these measures, education and awareness are also crucial. Moreover, by educating people about the importance of wildlife and the consequences of losing biodiversity, conservation techniques efforts can gain stronger public support, ultimately leading to lasting change.
How Conservation Efforts Impact Ecosystems and Humans
Protecting wildlife doesn’t just help animals, it helps us too. Healthy ecosystems provide clean air, fresh water, and fertile soil for growing food. The interconnectedness of nature means that preserving one part of it ultimately helps keep our entire environment stable. Imagine a spider web. Take away one part, and the entire thing weakens. Conservation helps ensure the web stays intact.
Understanding Conservation Techniques and Resource Management
Conservation Techniques: Sustainable Use of Natural Resources
Resource management in conservation techniques means using natural resources in a way that ensures they last for future generations. For example, instead of cutting down all the trees in a forest for timber, sustainable management involves taking only what we need and planting new trees in their place. This ensures that the forest, and all the animals relying on it, can survive.
Conservation Techniques: Balancing Human Needs with Conservation
People need resources to survive, like wood for building homes or fish for food. The challenge is balancing our needs with the health of the environment. Conservation resource management aims to find ways to use resources without destroying the habitats that wildlife depend on. It’s about making choices today that won’t leave us empty-handed tomorrow.

Conservation Techniques: The Importance of Habitat Protection for Biodiversity
Conservation Techniques: How Habitat Loss Leads to Species Extinction
When habitats are destroyed, like forests being cleared for farming, animals lose their homes. Without shelter, food, and a safe place to breed, many species can’t survive. Habitat loss is a leading cause of extinction.
For example, orangutans are losing their forest homes in Southeast Asia, pushing them to the brink of extinction. This also disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, affecting not only the animals directly impacted but also the plants, insects, and other organisms that share their habitat. Moreover, fragmented habitats make it difficult for species to migrate, find mates, or access seasonal resources.
As a result, genetic diversity often decreases, making populations more vulnerable to diseases and environmental changes. Therefore, addressing habitat loss requires comprehensive approaches like sustainable agricultural practices, forest management, and the establishment of protected areas that provide safe spaces for wildlife to thrive. Additionally, encouraging reforestation and involving local communities in habitat protection are also key steps in mitigating the effects of habitat destruction.
Conservation Techniques: Protected Areas and Wildlife Corridors
One key strategy in conservation techniques is creating protected areas. National parks, wildlife reserves, and even smaller conservation techniques areas give animals safe spaces where they can live without human interference.
These protected areas serve as refuges where species can breed, feed, and live in relatively stable conditions, away from the threats of habitat destruction and human exploitation. Moreover, wildlife corridors, which connect these safe areas, allow animals to migrate and access a broader range of resources, essential for their survival.
Corridors are especially important for maintaining genetic diversity, as they enable animals from different populations to meet and breed, reducing the risks associated with inbreeding. Furthermore, corridors help species adapt to environmental changes by providing paths to new habitats if their current ones become unsuitable due to climate change or other factors. Therefore, establishing these interconnected areas is crucial for ensuring that wildlife populations are not isolated, ultimately giving them a better chance to adapt, survive, and thrive.
Conservation Techniques: Strategies for Successful Wildlife Conservation
Conservation Techniques: Anti-Poaching Initiatives
Poaching, the illegal hunting of animals, remains one of the biggest threats to wildlife. Anti-poaching teams, equipped with training and technology, are critical in protecting endangered species. These teams use advanced tools such as drones, camera traps, and satellite imagery to monitor and track poaching activities, often working around the clock in harsh conditions.
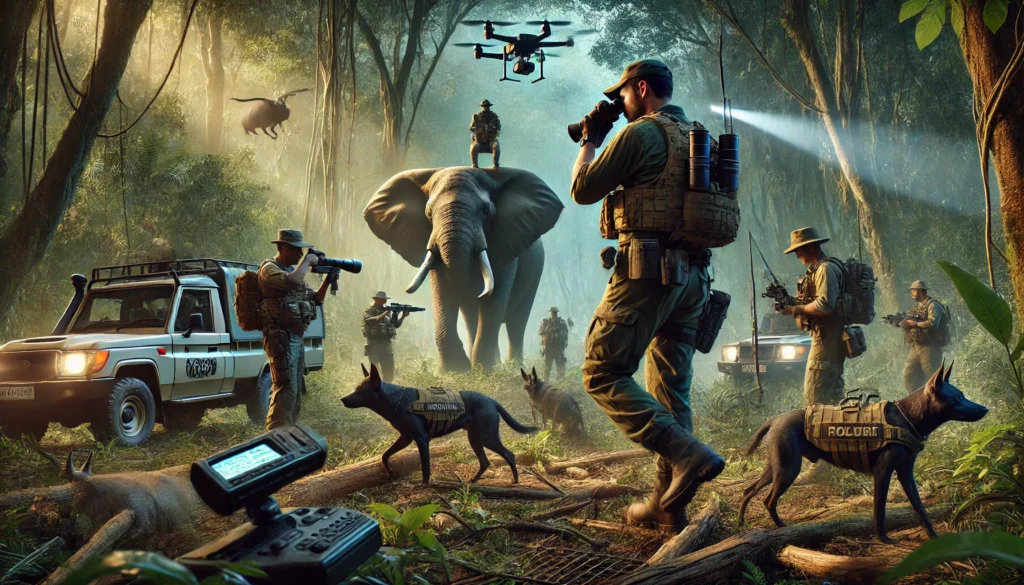

Furthermore, local communities play a vital role; offering economic alternatives and raising awareness about conservation encourages them to actively participate in anti-poaching efforts. For example, saving African elephants largely depends on communities stopping poachers, as their ivory is highly sought on the black market.
Additionally, education and awareness campaigns aimed at reducing demand for ivory products are also key elements in combating poaching. In regions like Africa and Asia, where poaching remains a persistent issue, a combination of strict enforcement, community involvement, and international pressure is essential to make a lasting impact.
Conservation Techniques: Captive Breeding and Rewilding Programs
Captive breeding involves raising endangered species in controlled environments, like zoos, and then releasing them back into the wild. This approach helps maintain genetic diversity and ensures that vulnerable species have a chance to increase their populations.
Rewilding goes further by helping species reestablish themselves in areas they once roamed freely, aiming to restore entire ecosystems to their natural state. Importantly, rewilding is not just about reintroducing animals but also about reviving the natural processes that sustain biodiversity. The California condor, for instance, was brought back from the brink of extinction through these methods, thanks to dedicated breeding programs and habitat protection.
These efforts included fostering condor chicks in captivity and teaching them survival skills before their release. Today, the California condor soars once again in its native skies, illustrating the success that careful planning and collaboration between scientists, conservationists, and local communities can achieve. Such projects serve as powerful reminders of what can be accomplished when we prioritize conservation techniques.
Community Involvement in Habitat and Resource Management
Role of Indigenous Communities
Indigenous communities have been living in balance with nature for centuries, often understanding local ecosystems better than anyone else. Involving these communities in conservation techniques efforts can lead to more effective strategies.
Their knowledge of medicinal plants, animal behaviors, and seasonal changes provides a unique perspective that benefits conservation techniques work. Furthermore, indigenous practices, which are rooted in sustainability, offer valuable insights into managing natural resources without causing environmental harm. For example, many indigenous groups have traditional methods for controlled burning that reduce wildfire risks and promote the health of certain ecosystems.
Additionally, these communities often act as stewards of large tracts of land that have remained relatively undisturbed. By recognizing and integrating indigenous rights and land stewardship in conservation techniques policies, we can protect not only biodiversity but also cultural heritage. Such collaboration helps build trust and ensures that conservation techniques initiatives are inclusive, respectful, and effective in the long term.
Community-Led Conservation Initiatives
Some of the most successful conservation techniques projects involve local communities taking charge of their natural resources. By empowering locals to protect their environment, conservation techniques become more sustainable. This community-based approach ensures that the people closest to the problem are part of the solution, which enhances the effectiveness of conservation measures.
When local people are involved, they develop a sense of ownership, which often leads to better protection and stewardship of natural habitats. Furthermore, this approach not only helps wildlife but also provides economic benefits through sustainable tourism and employment opportunities. In many cases, locals are trained as guides, park rangers, or artisans, which contributes to their livelihoods while promoting conservation awareness.
Namibia is a great example, where communities manage wildlife and benefit from tourism, incentivizing healthy animal populations. Through communal conservancies, locals earn income from ecotourism and regulated trophy hunting, aiding species recovery like the black rhino and desert-adapted elephants. Ultimately, this community-led approach shows conservation can be both environmentally and economically beneficial, serving as a model for other regions.
Examples of Successful Conservation Projects Around the World
- Yellowstone National Park (USA): The reintroduction of wolves to Yellowstone helped rebalance the entire ecosystem, reducing overgrazing by deer and allowing plant life to recover.
- Mountain Gorilla Conservation (Rwanda): Efforts to protect mountain gorillas through ecotourism have not only saved the species from extinction but also boosted the local economy.
Threats to Wildlife Habitats and How to Mitigate Them
Deforestation and Urban Expansion
Deforestation and urban expansion are two major threats to wildlife habitats worldwide. When forests are cut down for timber or cleared to make way for new housing developments, countless animals lose their natural habitats. This displacement often leads to decreased populations, as species struggle to find food, shelter, and suitable conditions to breed.
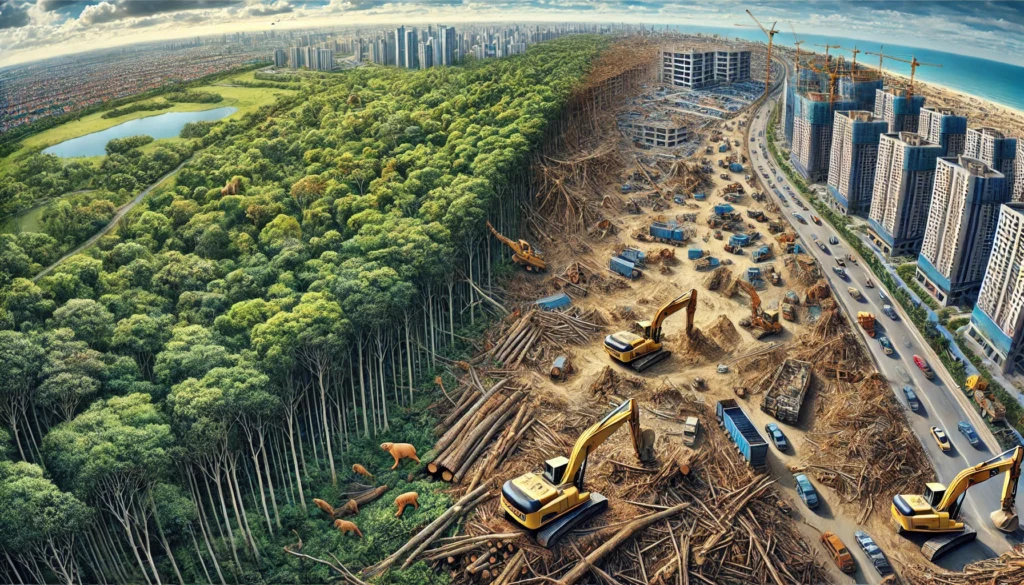

Moreover, fragmented habitats caused by urban sprawl limit the movement of wildlife, making it difficult for species to access the resources they need. To mitigate these impacts, practices like reforestation, replanting trees in areas where forests have been cleared, are crucial. Furthermore, urban planning that integrates green spaces, wildlife corridors, and sustainable development practices can also help balance human expansion with the needs of the natural world.
When forests are cut down for timber or land is cleared for housing, the animals that live there are left without a home. To mitigate this, practices like reforestation, planting trees where they have been cut, can help restore habitats. Urban planning that takes wildlife into account can also create greener cities, which benefit both people and animals.
Pollution and Its Impact on Habitats
Pollution, whether it’s plastic waste in the oceans or toxic chemicals in rivers, is devastating for wildlife. It disrupts ecosystems, harms animals, and can lead to long-term environmental damage. For instance, marine animals often ingest plastic waste, mistaking it for food, which can result in fatal blockages or toxic poisoning.
Simple actions, like reducing plastic use and properly disposing of waste, can make a big difference. Cleaner rivers lead to healthier fish populations, which benefits not only the ecosystem but also the communities relying on those fish for food.
Reducing chemical runoff from agriculture and industry improves water quality, ensuring clean water for wildlife and people. Furthermore, advocating for stronger pollution regulations and supporting clean-up initiatives helps reduce pollution’s harmful impact on habitats.
Role of Governments and NGOs in Wildlife Conservation
Governments and NGOs play a big role in funding and managing conservation techniques projects. They create laws that protect wildlife, fund research, and help establish protected areas. Organizations like the WWF (World Wildlife Fund) are instrumental in raising awareness and driving conservation techniques efforts globally.
Governments often set policies that regulate hunting, logging, and land use to minimize their impact on wildlife habitats. NGOs, on the other hand, can provide the expertise, funding, and community outreach that make conservation techniques projects successful.
By bringing together science, policy, and community involvement, both governments and NGOs develop a comprehensive approach to conservation techniques. This strategy not only addresses immediate threats but also paves the way for long-term sustainability. Through collaborative efforts, they ensure that conservation is effective in both the short and long term, creating a balanced solution for environmental challenges.
Future Outlook for Wildlife Conservation and Habitat Protection
The future of wildlife conservation techniques depends on collective action. Governments, NGOs, communities, and individuals all have roles to play. The challenges are significant, climate change, habitat loss, and poaching, but they aren’t insurmountable. With sustained effort, technological innovation, and community involvement, we can ensure that wildlife continues to thrive.
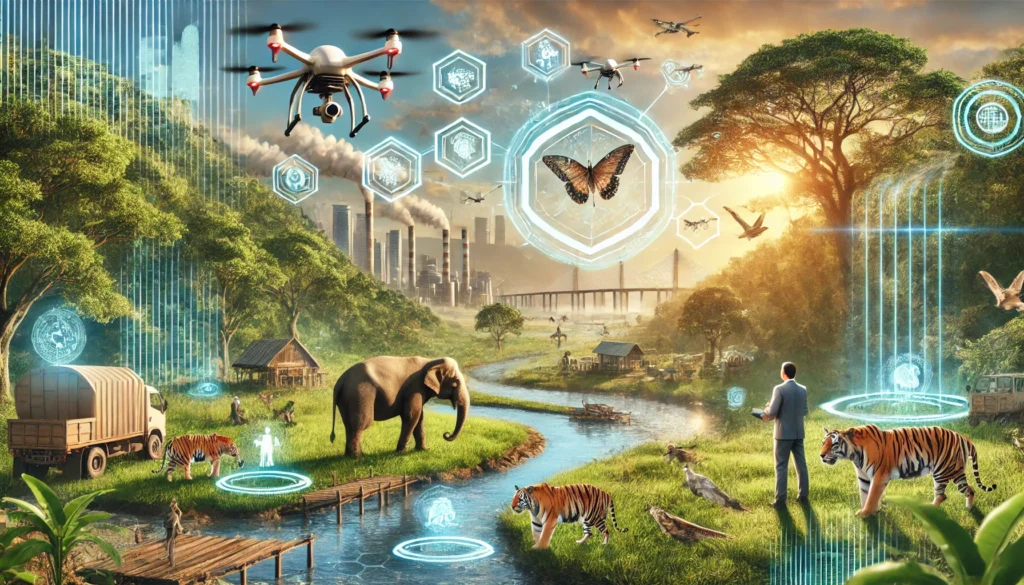

Technological advances like satellite monitoring and camera traps provide valuable data, helping conservationists track animals and detect illegal activities. Additionally, promoting education across schools, communities, and media raises awareness about the importance of conservation efforts.
By encouraging younger generations to take an interest in wildlife, we create a culture that values and protects nature. Collaboration across borders, such as international treaties and agreements, also plays a crucial role, as many species migrate and need protection across multiple countries. Only through a united, informed, and proactive approach can we overcome the challenges ahead.
How Can You Contribute to Wildlife Conservation?
Small actions can have a big impact. Reducing plastic use, supporting wildlife charities, and even just spreading awareness are all steps in the right direction. The choices you make every day, like buying sustainable products or reducing energy consumption, can help protect the natural world.
For example, choosing reusable bags and water bottles instead of single-use plastics reduces waste that harms wildlife. Additionally, supporting conservation groups through donations or volunteering helps fund critical projects protecting endangered species and habitats. Furthermore, planting native plants in your garden creates a safe space for local wildlife, offering food and shelter for birds, insects, and small mammals.
Even seemingly small efforts like voting for policies that prioritize environmental protection can drive change on a larger scale. Every little step matter, and collectively, these actions can lead to significant positive outcomes for wildlife conservation techniques.
FAQs about Wildlife Conservation
What are wildlife conservation techniques and why are they important?
Wildlife conservation techniques involve protecting animal species and their habitats to maintain ecological balance.
How does habitat protection help endangered species?
Habitat protection provides a safe environment for species to live, breed, and find food.
What are the key strategies for successful wildlife conservation techniques?
Key strategies include anti-poaching initiatives, captive breeding, rewilding program, and involving local communities in conservation techniques efforts.
What is resource management and how does it relate to conservation techniques?
It is about using natural resources sustainably so they are available for future generations.
How communities can be involved in conservation techniques efforts?
Communities can play a role by participating in conservation techniques projects, managing local resources, and benefiting from eco-friendly tourism.
What are the biggest threats to wildlife habitats today?
The biggest threats include deforestation, urban expansion, pollution, climate change, and poaching.
How do governments support wildlife conservation techniques?
Governments support conservation techniques by creating protected areas, enacting laws against poaching, funding, and collaborating with NGOs.
What are some examples of successful wildlife conservation techniques projects?
Successful projects include the reintroduction of wolves in Yellowstone National Park, and the conservation techniques of mountain gorillas in Rwanda.
What are wildlife corridors and why are they important?
Wildlife corridors are natural routes that connect different habitats, allowing animals to move safely between them.
How can individuals contribute to wildlife conservation techniques?
Individuals can contribute by reducing waste, spreading awareness, and making environmentally conscious lifestyle choices.
Wrap-Up: The Time to Act is Now
Wildlife conservation techniques are about more than saving animals; it’s about ensuring our own survival. Every action counts, and the more informed we are, the better choices we make. Together, we can protect the wonders of our planet for future generations.